Water Volume
Currently, about 1.6 km3 of water flow into the Sea each year, the inflows come from Imperial Valley, Mexico, Coachella Valley, and local runoff. (Cohen, 2014).Right now the amount of water entering the Sea equals the amount of water evaporating. However, when Imperial Valley transfers water to San Diego, the amount of water entering the Sea will become less than the amount of water being drained. Why is it bad when water flow rate is reduced? Reduced water flow into the Sea can lead to a catastrophe — the size of the Sea will shrink, the salinity will go up, and wild lives will be affected. Imagine if you have a bowl full of salt water, and a hole appears, causing water to escape and leaving only salt in the bowl. The Salton Sea is a big bowl of salt water. As water flow rate continues to decrease, the sea surface will drop to 20 feet after 2017, which will shrink the Sea’s volume by 60%! (Cohen, 2006). By that time, salinity will be tripled, and fish will be gone due to poor water quality.
As the Salton Sea continues to dry up, it will have negative impact the region in terms of public health, economy, and ecology. The residents’ health is at higher risk of getting asthma, cardiac disease, and lung cancer(Cohen, 2014). Studies show that high concentration of dust lung negatively affects function growth (Gauderman, 2000). Agricultural productivity will decrease because the temperature and humidity will no longer be appropriate for farming without the buffering of the Sea. Recreational revenues will drop because of the strong odors and dusty environment, which prevent people from coming here and play. Ecological value will also decrease, as the Salton Sea – the habitat for hundreds of thousands of birds – deteriorates.
Salinity
Currently, the salinity of the Salton Sea is ~46.5 g/L, that means, there are 46.5 grams of salt dissolved in every liter of water. That is 33% saltier than ocean water (Cohen, 2014). Salinity continues to go up every year as 4 million metric tons of salts continue to enter the Salton Sea. (Cohen, 2014). Water flows into the Salton Sea mostly from the Alamo and New rivers in Imperial Valley. Alamo River water contains agricultural drain water, and New River water contains agricultural drainage, which has high concentrations of nutrients and pesticides. Many of the contaminants entering the Sea just settle and concentrate within the Sea. The concentrated nitrogen, phosphorus, selenium, and pesticide residues foster to production of hydrogen sulfide and ammonia — which cause fish kills and odors.
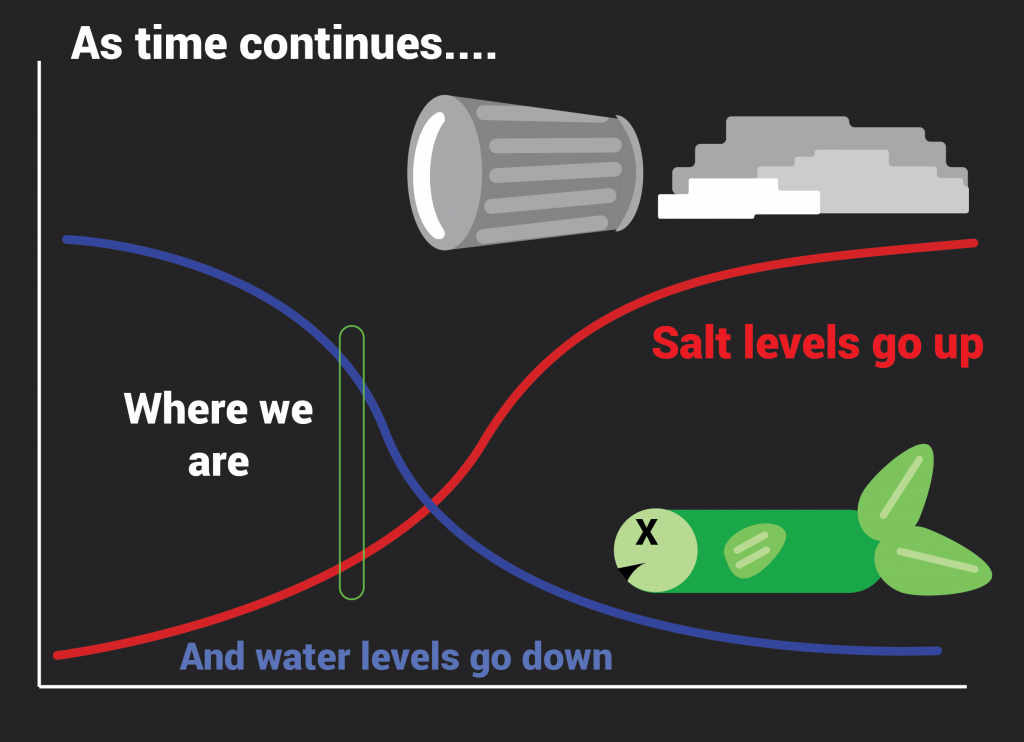
As time goes on, the water level is likely to decrease causing the salt concentration to become increasingly uninhabitable. The death of multiple species of wildlife would be tragic for the environment
Information cited from
Cohen, M. J. (2014, September). Hazard’s Toll: The Costs of Inaction at the Salton Sea. Retrieved March 16, 2016, from
http://pacinst.org/publication/hazards-toll/
http://pacinst.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/21/2014/09/PacInst_HazardsToll.pdf
Cohen, M. J. (2006). Hazard: The Future of the Salton Sea with No Restoration Project. Retrieved March 16, 2016, from
http://pacinst.org/publication/restoration-project-critical-to-salton-seas-future/
Gauderman, W.J & McConnell, R. & Gilliland, F. (2000). Association between Air Pollution and Lung Function Growth in Southern California Children. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Vol. 162, No. 4 (2000), pp. 1383-1390.
doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.162.4.9909096. Retrieved March 16, 2016, from
http://www.atsjournals.org/doi/pdf/10.1164/ajrccm.162.4.9909096

